Biotech Buzz #3: Did scientists find the cause of anxiety? Using electricity to heal wounds & more
Plus new formatting & what to expect in the future from this newsletter
Welcome to the third edition of Biotech 🐝 ! As I mentioned last week, we would be testing a new format for the newsletter, with the major sections centering around Synthetic Biology (gene editing, materials engineering etc.), AI, & Disease Treatments/Longevity.
We have some exciting articles for you this week, covering a range of topics from cutting-edge research on gene-brain studies to wearable patches that can painlessly deliver drugs through the skin. We also explore the use of electricity to heal wounds faster and a new pathway for clearing misfolded proteins. Additionally, we dive into the secrets of hydrogen's hidden phase and the application of artificial intelligence in radiology. Lastly, we take a look at some intriguing studies on sex differences in bitterness perception and the use of dirty diapers to gain insights into babies' gut health. Let's dive in!
Here is my Twitter.
Synthetic Biology
Article: Gene in the brain can put brakes on anxiety, discover scientists
DEFINITIONS:
miRNA: miRNA stands for microRNA, which are small, non-coding RNAs that play a crucial role in gene regulation in various biological processes.
Pgap2: PGAP2 "Post-GPI Attachment to Proteins 2" is a protein-encoding gene which may be involved in protein modification and cell signaling.
SUMMARY:
An international team of scientists has discovered a gene in the brain driving anxiety symptoms.
Importantly, the team showed that modification of the gene reduced anxiety levels, offering a novel drug target for anxiety disorders.
MiRNAs are strategically poised to control complex neuropsychiatric conditions such as anxiety.
The miR483-5p/Pgap2 pathway identified in this study, which exerts anxiety-reducing effects, offers a huge potential for the development of anti-anxiety therapies for complex psychiatric conditions in humans.
My Take:
The study presents a huge development in anti-anxiety therapies, as the discovery of miR483-5p/Pgap2 pathway proves to offer a solution for complex psychiatric conditions in humans.
DEFINITIONS:
Transdermal drug delivery: the delivery of drugs through the skin.
SUMMARY:
The researchers have developed a wearable patch that applies painless ultrasonic waves to the skin, creating tiny channels that drugs can pass through.
This approach could lend itself to delivery of treatments for a variety of skin conditions, and could also be adapted to deliver hormones, muscle relaxants, and other drugs.
In tests, they showed that when they delivered niacinamide using the ultrasound patch, the amount of drug that penetrated the skin was 26 times greater.
With further modifications to increase the penetration depth, this technique could be used for drugs that need to reach the bloodstream.
MY Take:
This wearable patch could be a revolution for people suffering from skin conditions and premature skin aging.
With the modifications, people could benefit from other drugs such as hormones, muscle relaxants, and those that have to reach the bloodstream painlessly.
Article: Bacterial ‘Nanosyringe’ Could Deliver Gene Therapy to Human Cells
DEFINITIONS:
Gene-editing: a type of genetic engineering in which DNA is inserted, deleted, modified or replaced in the genome of a living organism.
SUMMARY:
The new syringe technology holds promise for scientists interested in delivering gene editing enzymes to cells, including the genes that are mutated in genetic disorders.
The Photorhabdus syringe has been adapted to attach to human cells and inject large proteins into them, and can be engineered to attach to receptors on certain cancer cells.
The researchers tailored the syringe's tail fibers to recognise surface markers on different cell types and found that packing the system with various protein payloads was possible by using a tag to mark them as the ammunition.
Longevity and Disease Treatments
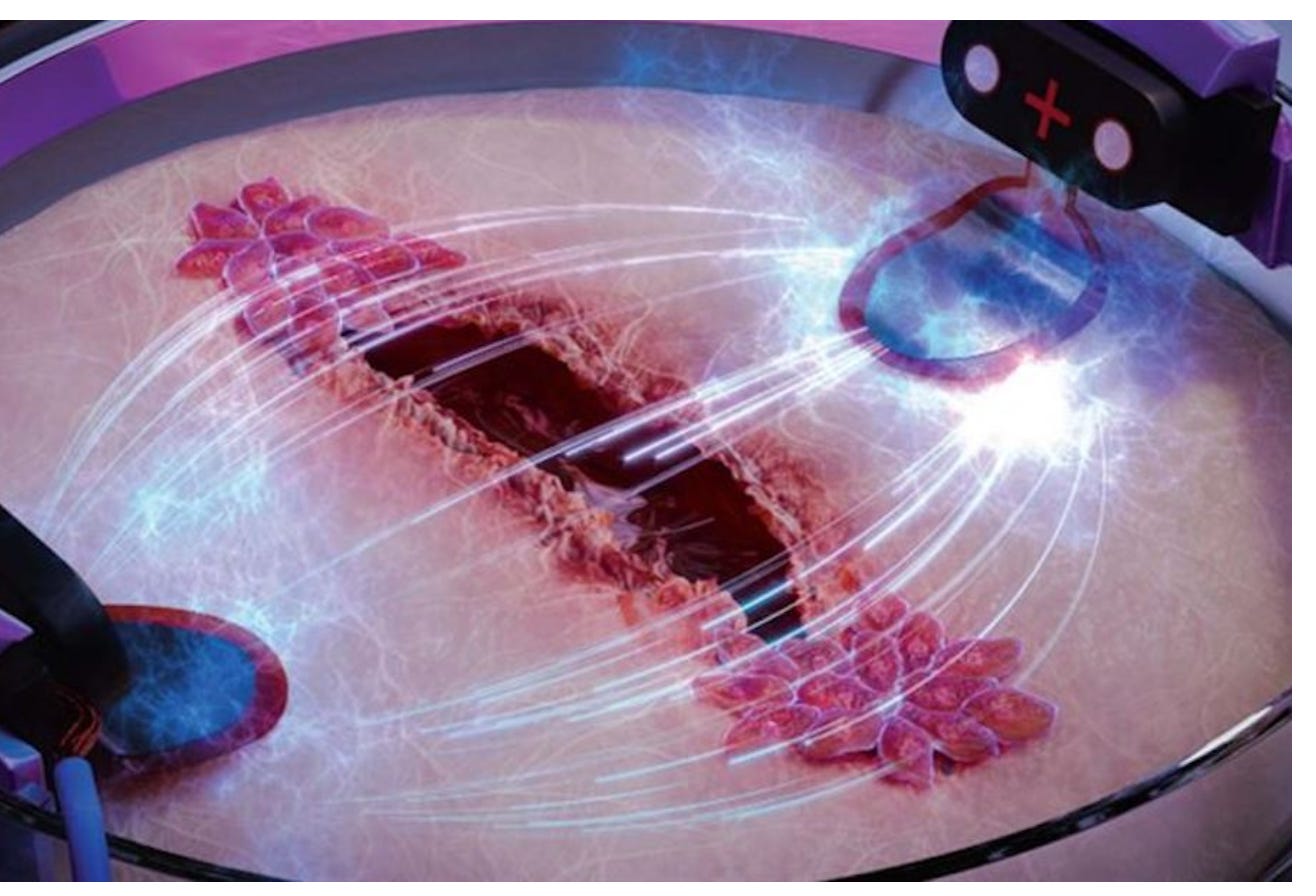
Article: Electricity can heal wounds three times faster
DEFINITIONS:
Electrotaxis: the directional movement of cells in response to electric fields.
SUMMARY:
The researchers found that electric stimulation can heal wounds three times faster.
Chronic wounds affect diabetic and elderly patients and can lead to amputation.
Electrically guiding cells using the principle of electrotaxis can help wounds heal faster.
The researchers received a grant to continue their research and develop wound healing products for consumers.
My Take:
This is exciting news for those suffering from chronic wounds, particularly diabetic and elderly patients. This could also be big news for sports injuries. Imagine a world where injuries don’t affect people for extended periods of time?
Article: New injectable cell therapy could resolve osteoarthritis
DEFINITIONS:
Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint system that typically results from mechanical or traumatic stress in the joint, leading to damaged cartilage that cannot be repaired naturally.
Cartilage: a flexible connective tissue found in many areas of the body, including joints, that provides shape and support and can help to protect against damage.
SUMMARY:
Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) scientists have created a promising injectable cell therapy to treat osteoarthritis that both reduces inflammation and also regenerates articular cartilage.
Osteoarthritis is a disease of the joint system that affects more than 520 million people worldwide.
A cell therapy was designed that can overcome the inflammatory environment and also regenerate cartilage.
This combination of cells simultaneously treat inflammation, cartilage degradation etc.
Once treated, the patients experienced improved quality of life, ability to participate in recreational activities, and reduced pain.
Article: This Longevity Study Across 5 Species Found a New Pathway to Reverse Aging
DEFINITIONS:
Transcription is the first step in turning genetic material into proteins.
It turns DNA into RNA that then shuttles the genetic information to other parts of the cell to make proteins.
SUMMARY:
A new study in Nature has identified a critical molecular process that powers every single cell inside the body and degrades with age.
In all five species tested, as the organism grew older, transcription – the first step in turning genetic material into proteins – sped up, but like trying to type faster when blindfolded, error rates shot up.
Two interventions that extend lifespan, the inhibition of insulin signaling and caloric restriction, were shown to slow down transcription across several species, including mice.
Similarly, genetic mutations that reversed sloppy transcription behaviour also extended lifespan in worms and fruit flies, and boosted human cells’ ability to divide and grow.
My Take:
It seems like ‘Longevity’ is the hottest area in biotech. Very curious to see what comes out of this field in the coming years.
Article: Study finds new pathway for clearing misfolded proteins | Stanford News
DEFINITIONS:
Misfolded Proteins: are proteins that are unable to perform their normal functions within cells.
Organelle: An organelle is a tiny structure within a cell that carries out specific functions within the cell.
SUMMARY:
Stanford researchers defined a novel cellular pathway – including a “dump site” – for clearing misfolded proteins from cells.
The pathway is a potential therapy target for age-related diseases like Alzheimer’s, Huntington’s, and Parkinson’s diseases.
The team identified the “garbage dump” site as the intersection of the nucleus and the vacuole – an organelle full of enzymes for degrading proteins – and showed that misfolded proteins in this “garbage dump” site are moved into the inside of the vacuole for degradation.
Artificial Intelligence
DEFINITIONS:
Metabolism: biological transformation by which most drugs undergo a change in their chemical structure in the body to produce the expected therapeutic effects of a certain drug and be more easily eliminated from the body
Drug excretion: refers to the elimination of drugs or their metabolites from the body
SUMMARY:
The development of AI models for drug metabolism and excretion prediction holds great promise for improving drug R&D.
Collaboration and data sharing among researchers, pharmaceutical companies, and regulatory agencies can aid in the improvement of data quality and availability for AI model development
In addition to using existing explanatory AI methods such as feature attribution, instance-based, graph-convolution-based, and self-explanatory methods [123], efforts are being made to develop new methods to ensure transparency, safety, efficacy, and reliability in clinical settings, and maintain public trust in AI technology.
DEFINITIONS:
Data Algorithm Training Output (DATO) method: a consistent and systematic approach to discussing the details and potential limitations of artificial intelligence research, by considering the Data, Algorithm, Training, and Output of AI processes.
Evidence-based practice (EBP): the integration of clinical expertise, patient values and preferences, and best available evidence to make clinical decisions and care recommendations.
SUMMARY:
As the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in radiology increases, it is necessary for radiologists and related professionals to review not only clinical radiological literature but also research using AI methods.
Evidence-based practice (EBP) can be applied to AI using the data algorithm training output (DATO) method, which considers Data, Algorithm, Training, and Output in the use of AI to answer a question.
The DATO method is a simple systematic approach to understanding complex AI research and allows for a more evidence-based approach to incorporating AI into radiology practice.
DEFINITIONS:
Large Language Models: models that are capable of generating human-like responses to user prompts.
SUMMARY:
The study evaluated ChatGPT's performance on standardized admission tests in the United Kingdom to understand its potential as an innovative tool for education and test preparation.
Chat GPT shows promise as a supplementary tool for subject areas and test formats that assess aptitude, problem-solving and critical thinking, and reading comprehension.
The study highlights Chat GPT's limitations in areas such as scientific and mathematical knowledge and applications.
The authors hope their results serve as a catalyst for discussions on how current education can foster the development of more effective learning tools and strategies using artificial intelligence tools like Chat GPT.
My Take:
These LLMs or Large Language Models continuously blow my mind & I think that they will have a large place in medicine in the next 5-10 years.
Article: Generating Topic Pages for Scientific Concepts Using Scientific Publications
DEFINITIONS:
Topic Pages: a publicly available knowledge base for scientific concepts with their definitions, most relevant concepts, and snippets providing more context around them.
Sci BERT: a pre-trained language model that specializes in scientific text.
SUMMARY:
Topic Pages is a knowledge base for scientific concepts with their definitions and relevant snippets providing more context around them.
It has over 363,000 topic pages in 20 different scientific domains and is popular among researchers and students, with more than 23 million unique visitors per month.
The pipeline for generating Topic Pages can be used on top of any document collection with a taxonomy to build a similar resource in any domain.
The Sci BERT model used for definition extraction still needs improvement for domains such as Social Sciences as it is pre-trained on mostly biomedical articles.
MISC
Article: Dirty diapers yield data on babies' gut biome - The Washington Post
SUMMARY:
An international team of researchers has found more than 10,000 new viruses in infant feces.
The study looked at the feces of 647 healthy Danish 1-year-olds who were enrolled in long-term asthma and chronic inflammatory disease studies.
The viruses were ten times more abundant than the bacterial species in the children's feces, and ninety percent of them were bacteriophages.
The researchers believe that kids' intestines develop a web of viruses, which protect against chronic illnesses like asthma and diabetes.
My Take:
This groundbreaking research exploring infant microbiomes is critical to understanding how our bodies build immunity and how viruses can play a role in preventing chronic illness. It seems like we learn more about the microbiome everyday!
Article: Genetic map of Tasmanian devil cancers hints at their future evolution
DEFINITIONS:
There are two contagious facial tumours in the Tasmanian Devil, Devil facial tumour 1 (DFT1) and Devil facial tumour 2 (DFT2), which are both spread by biting.
SUMMARY:
In a new study, researchers have analysed the genetic makeup of facial cancers in Tasmanian Devils that have been prevalent for three decades.
The research has now provided insight into the cancers' past, origins, and how they have evolved, providing clues about how they could spread in the future.
This enables researchers to predict how they are likely to affect Tasmanian devil populations in the future.
Previous research showed that Tasmanian devil populations are becoming more resilient.